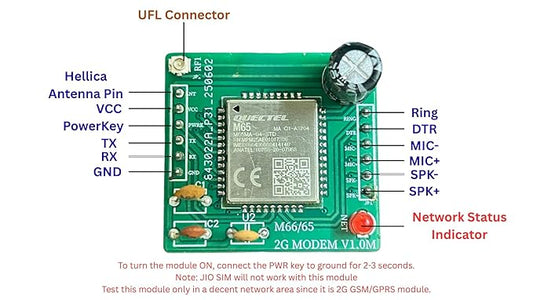
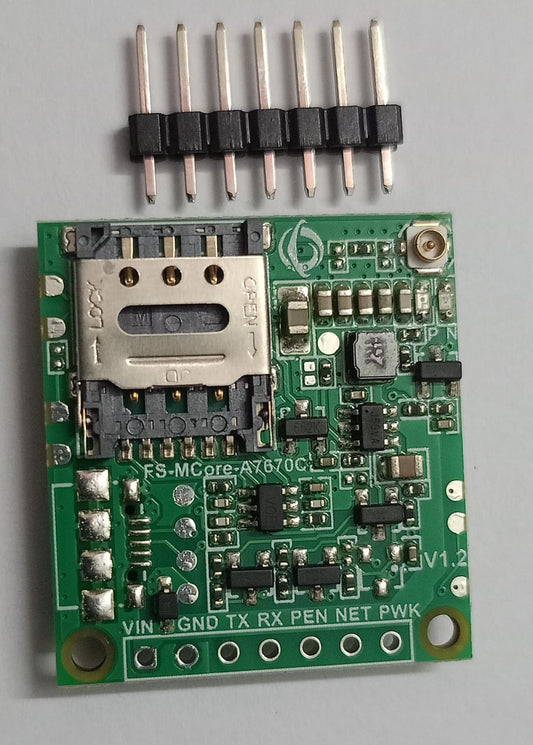
Build. Create. Innovate. With Voltros
Explore our user-friendly catalog and find the perfect components for your circuit boards, robotics, DIY gadgets, and more. With Voltros, you're not just buying parts; you're getting the reliable foundation for your next great creation